The Future is Self-Driving
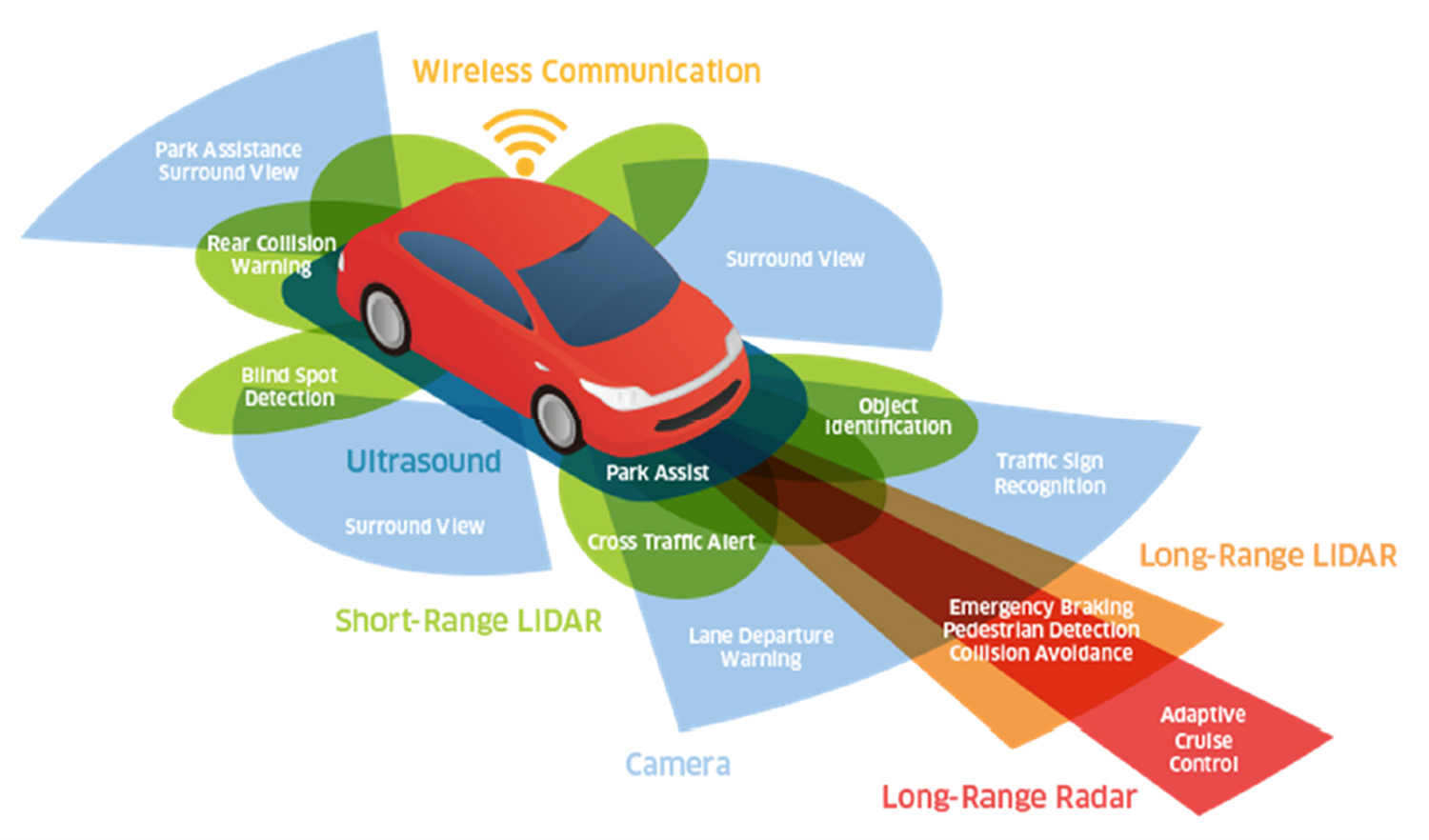
As we move closer to a world with self-driving cars, three important technologies help these vehicles “see”: Lidar, Radar, and Cameras. These systems are crucial for understanding the environment, ensuring safe driving, and avoiding obstacles. Let’s break down how each technology works and see which one is best for autonomous driving.
Lidar: The Laser Vision
Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) gives cars a detailed view of their surroundings. It works by sending out laser beams and measuring how long it takes for them to bounce back. This helps create a precise 3D map of the area.
How Lidar Works:
• Sends out millions of laser beams every second
• Measures how long it takes for each beam to return
• Creates a detailed 3D map of the environment
Advantages:
Very accurate—can detect objects very close
Works well both day and night
Great at judging distances
Limitations:
More expensive than other sensors
Can struggle in heavy rain, fog, or snow
—
Cameras: The Human Eye Replacement
Cameras act like the eyes of self-driving cars. They capture images of colors, shapes, and textures, which help the car recognize road signs, pedestrians, and traffic lights.
How Cameras Work:
• Take 2D pictures of the surroundings
• Use AI and Machine Learning to recognize objects
• Help with lane detection, reading signs, and spotting obstacles
Advantages:
Cheaper than Lidar
Can read traffic lights and road signs
Provides rich visual details
Limitations:
Performance drops in low light or bad weather
Not as good at measuring distances compared to Lidar and Radar
Radar: The All-Weather Guardian
Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging) uses radio waves to detect objects, even in tough weather. It is commonly used in features like adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance.
How Radar Works:
• Sends out radio waves that bounce off objects
• Measures how far away and how fast objects are moving
• Works well in fog, rain, and darkness
Advantages:
Reliable in all weather conditions
Good at detecting moving objects
Can see far distances
Limitations:
Lower detail compared to Lidar
Can’t identify colors or small details
—
Which Technology is Best?
Each technology has its own strengths and weaknesses. That’s why most self-driving cars use all three:
Lidar + Cameras + Radar = A Safer Self-Driving System!
By combining Lidar’s accuracy, Camera’s detail, and Radar’s reliability, self-driving cars can navigate safely and effectively on the roads.


Leave a Reply